ideas
Paul Ehrlich gave a talk at Stanford titled “Can a Collapse be Avoided”? Ehrlich is a biologist but his interests spread to Economics and Technology as well. The “collapse” of his talk is the catastrophe that, according to most climate scientists, is rapidly approaching. He listed eight major environmental problems and briefly discussed each. Some of them need no introduction (extinction of species, climate change, pollution) but others are no less catastrophic even though less advertised.
For example, global toxification: we filled the planet with toxis substances, and therefore the odds that some of them interact/combine in some deadly chemical experiment never tried before are increasing exponentially every year. There is no known way to fix something like that. We know how to fix pollution and carbon emissions and so forth (if we wanted to), but science would not know how to deal with a chemical reaction triggered by the combination of toxic substances in the soil. The highlight of the talk for me was the emphasis on “non-linearity”. Many scientists point out the various ways in which humans are hurting our ecosystem, but few single out the fact that some of these ways may combine and become something that is more lethal than the sum of its parts.
Another interesting point that is not widely recognized is that the next addition of one billion people to the population of the planet will have a much bigger impact on the planet than the previous one billion. The reason is that human civilizations already used up all the cheap, rich and ubiquitous resources. Naturally enough, humans started with the cheap, rich and ubiquitous ones, whether forests or oil wells. A huge amount of resources is still left, but those will be much more difficult to harness. For example, oil wells have to be much deeper than they used to. Therefore one liter of gasoline today does not equal one liter of gasoline a century from now: a century from now they will have to do a lot more work to get that liter of gasoline. That was the second key point that struck me: it is not only that some resources are being depleted, but even the resources that will be left are, by definition, those that are difficult to extract and use (a classic case of diminishing margin of return).
The bottom line of these arguments is that the collapse is not only coming, but the combination of the eight factors plus the internal combinations in each of them make it likely that it is coming even sooner than pessimists predict.
{ Piero Scaruffi | Continue reading }
future, ideas, incidents | October 25th, 2012 11:48 am

How could I successfully kill a clone that is always thinking the exact same thing I am?
[…]
Kill yourself.
{ Quora | more answers }
photo { Mark Powell }
ideas, photogs | October 24th, 2012 2:58 pm

Over time, we have grown increasingly vulnerable to natural disasters. Each decade economic losses from such disasters more than double as people continue to build homes, businesses, and other physical infrastructure in hazardous places. Yet public policy has thus far failed to address the unique problems posed by natural disasters. […]
Drawing from philosophy, cognitive psychology, history, anthropology, and political science, this Article identifies and analyzes three categories of obstacles to disaster policy — symbolic obstacles, cognitive obstacles, and structural obstacles. The way we talk about natural disaster, the way we think about the risks of building in hazardous places, and structural aspects of American political institutions all favor development over restraint. Indeed, these forces have such strength that in most circumstances society automatically and thoughtlessly responds to natural disasters by beginning to rebuild as soon as a disaster has occurred.
{ SSRN | Continue reading }
photo { Ann James }
architecture, ideas, incidents | October 24th, 2012 2:52 pm

Adrian Wooldridge has an excellent column on how the advent of driverless cars might impact the global automotive industry and the broader economy. […]
When people are no longer in control of their cars they will not need driver insurance—so goodbye to motor insurers and brokers. Traffic accidents now cause about 2m hospital visits a year in America alone, so autonomous vehicles will mean much less work for emergency rooms and orthopaedic wards. Roads will need fewer signs, signals, guard rails and other features designed for the human driver; their makers will lose business too. When commuters can work, rest or play while the car steers itself, longer commutes will become more bearable, the suburbs will spread even farther and house prices in the sticks will rise. When self-driving cars can ferry children to and from school, more mothers may be freed to re-enter the workforce. The popularity of the country pub, which has been undermined by strict drink-driving laws, may be revived. And so on.
{ National Review | Continue reading }
photo { George Kelly }
economics, future, ideas, transportation | October 23rd, 2012 1:28 pm

A worrying trend has emerged in which a writer’s success has come to be measured by the number of views and comments elicited by his or her writing. Those same writers have, in a matter of a few years, adopted a new publishing ethos in which they post their thoughts, opinions, and writings on the plethora of blogging sites currently available. The generation of bloggers, many of whom started out as newspaper writers and later moved to electronic publishing, didn’t stop there—they expanded their commenting activity to their personal Facebook pages. […]
Facebook users find themselves in the position of a superstar or a prophet, needing to utter profound statements and expecting the cheers of the crowd. As it becomes easier and easier for people to connect, this loop tragically kills conversations and exchanges them for the proclamations of ignorant judges who know nothing of the world but their own personal narratives and verdicts.
{ e-flux | Continue reading }
ideas, media, social networks | October 22nd, 2012 10:56 am

This article examines cognitive links between romantic love and creativity and between sexual desire and analytic thought based on construal level theory. It suggests that when in love, people typically focus on a long-term perspective, which should enhance holistic thinking and thereby creative thought, whereas when experiencing sexual encounters, they focus on the present and on concrete details enhancing analytic thinking. Because people automatically activate these processing styles when in love or when they experience sex, subtle or even unconscious reminders of love versus sex should suffice to change processing modes. Two studies explicitly or subtly reminded participants of situations of love or sex and found support for this hypothesis.
{ Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin/SAGE | PDF }
ideas, psychology, relationships, sex-oriented | October 22nd, 2012 10:35 am

Implicit in the rationalist literature on bargaining over the last half-century is the political utility of violence. Given our anarchical international system populated with egoistic actors, violence is thought to promote concessions by lending credibility to their threats. In dyadic competitions between a defender and challenger, violence enhances the credibility of his threat via two broad mechanisms familiar to theorists of international relations. First, violence imposes costs on the challenger, credibly signaling resolve to fight for his given preferences. Second, violence imposes costs on the defender, credibly signaling pain to him for noncompliance (Schelling 1960, 1966). All else equal, this forceful demonstration of commitment and punishment capacity is believed to increase the odds of coercing the defender’s preferences to overlap with those of the challenger in the interest of peace, thereby opening up a proverbial bargaining space. Such logic is applied in a wide range of contexts to explain the strategic calculus of states, and increasingly, non-state actors.
From the vantage of bargaining theory, then, empirical research on terrorism poses a puzzle. For non-state challengers, terrorism does in fact signal a credible threat in comparison to less extreme tactical alternatives. In recent years, however, a spate of empirical studies across disciplines and methodologies has nonetheless found that neither escalating to terrorism nor with terrorism encourages government concessions. In fact, perpetrating terrorist acts reportedly lowers the likelihood of government compliance, particularly as the civilian casualties rise. The apparent tendency for this extreme form of violence to impede concessions challenges the external validity of bargaining theory, as traditionally understood. In Kuhnian terms, the negative coercive value from escalating represents a newly emergent anomaly to the reigning paradigm, inviting reassessment of it (Kuhn 1962).
That is the purpose of this study.
{ International Studies Quarterly | PDF }
related { Making China’s nuclear war plan | PDF }
fights, ideas, theory | October 19th, 2012 12:55 pm

If promises are binding, if they are cogent ways for people to bind themselves, there must be a reason to do as one promised. The paper is motivated by belief that there is a difficulty in explaining what that reason is, a difficulty that is not often noticed. It arises because the reasons that promising creates are content-independent. […]
To see the difficulty, think of an ordinary case: I have reason not to hit you, in fact there are a number of such reasons: it may injure you, it may cause you pain, invade your body, etc. They all depend on the nature of the action, its consequences and context. Now think of a reason arising out of a promise, say my reason to let you use my car tomorrow. The reason is that I promised to do so. But that very same reason applies to all my promises. If I promise to feed your cat next week, to come to your party, to send flowers in your name to your mother on Mother’s Day, to lend you my new DVD, or whatever the action I promise to perform (or to refrain from) the reason is the same: my promise. Of course, these are different promises. But normatively speaking they are the same, they are all binding on me because they are promises I made, regardless of what is the act promised. This is why they are (called) content-independent reasons. […]
One simple idea is that promises are binding qua promises (or rather that that is the only ground for their binding character of relevance here), and that they are promises because they are communications of an intention to undertake an obligation by that very communication, regardless of their content, regardless of which act or omission they are about. I suggested that there are exceptions; acts that one cannot promise to perform. For example, a promise (given in current circumstances) to exterminate homo sapiens or all primate species would not be binding. One may think that so long as such exceptions are rare they do not undermine the suggestion that promises are content-independent.
{ Joseph Raz/SSRN | Continue reading }
photo { Susan Worsham }
ideas, photogs, relationships | October 18th, 2012 1:52 pm

Usually people don’t agree with one another as much as they should. Aumann’s Agreement Theorem (AAT) finds:
…two people acting rationally (in a certain precise sense) and with common knowledge of each other’s beliefs cannot agree to disagree. More specifically, if two people are genuine Bayesian rationalists with common priors, and if they each have common knowledge of their individual posteriors, then their posteriors must be equal.
The surprising part of the theorem isn’t that people should agree once they have heard the rationale for each of their positions and deliberated on who is right. The amazing thing is that their positions should converge, even without knowing how the other reached their conclusion.
{ OvercomingBias | Continue reading }
images { 1. Garry Winogrand | 2 }
ideas | October 18th, 2012 12:48 pm

In 1935, Erwin Schrödinger devised an insidious thought experiment. He imagined a box with a cat inside, which could be killed at any moment by a deadly mixture of radiation and poison. Or it might not be killed at all. Both outcomes were equally probable.
But the consequence of thinking through this situation was much more shocking than the initial setup. According to quantum theory, there wasn’t just one cat inside the box, dead or alive. There were actually two cats: one dead, one alive—both locked into a state of so-called superposition, that is, co-present and materially entangled with one another. This peculiar state lasted as long as the box remained closed.
Macrophysical reality is defined by either/or situations. Someone is either dead or alive. But Schrödinger’s thought experiment boldly replaced mutual exclusivity with an impossible coexistence—a so-called state of indeterminacy.
But that’s not all. The experiment becomes even more disorienting when the box is opened and the entanglement (Verschränkung) of the dead and the live cat abruptly ends. At this point, either a dead or a live cat decisively emerges, not because the cat then actually dies or comes to life, but because we look at it. The act of observation breaks the state of indeterminacy. In quantum physics, observation is an active procedure. By taking measure and identifying, it interferes and engages with its object. By looking at the cat, we fix it in one of two possible but mutually exclusive states. We end its existence as an indeterminate interlocking waveform and freeze it as an individual chunk of matter.
To acknowledge the role of the observer in actively shaping reality is one of the main achievements of quantum theory.
{ e-flux | Continue reading }
ideas | October 17th, 2012 10:31 am
Linguistics | October 17th, 2012 8:33 am
When humans evolved bigger brains, we became the smartest animal alive and were able to colonise the entire planet. But for our minds to expand, a new theory goes, our cells had to become less willing to commit suicide – and that may have made us more prone to cancer.
When cells become damaged or just aren’t needed, they self-destruct in a process called apoptosis. In developing organisms, apoptosis is just as important as cell growth for generating organs and appendages – it helps “prune” structures to their final form.
By getting rid of malfunctioning cells, apoptosis also prevents cells from growing into tumours. […]
McDonald suggests that humans’ reduced capacity for apoptosis could help explain why our brains are so much bigger, relative to body size, than those of chimpanzees and other animals. When a baby animal starts developing, it quickly grows a great many neurons, and then trims some of them back. Beyond a certain point, no new brain cells are created.
Human fetuses may prune less than other animals, allowing their brains to swell.
{ NewScientist | Continue reading }
brain, health, science, theory | October 15th, 2012 11:53 am

When we read a text, we hear a voice talking to us. Yet the voice changes over time. In his new book titled Poesins röster, Mats Malm, professor in comparative literature at the University of Gothenburg, Sweden, shows that when reading older literature, we may hear completely different voices than contemporary readers did – or not hear any voices at all.
‘When we read a novel written today, we hear a voice that speaks pretty much the same language we speak, and that addresses people and things in a way we are used to. But much happens as a text ages – a certain type of alienation emerges. The reader may still hear a voice, but will not understand it fully and therefore risks missing important aspects,’ says Mats Malm.
{ EurekAlert | Continue reading }
books, psychology | October 15th, 2012 10:19 am

In 1964–to the disgust and dismay of most of my academic friends–I served as an economic adviser to Barry Goldwater during his quest for the Presidency. That year also, I was a Visiting Professor at Columbia University. The two together gave me a rare entree into the New York intellectual community. I talked to and argued with groups from academia, from the media, from the financial community, from the foundation world, from you name it. I was appalled at what I found. There was an unbelievable degree of intellectual homogeneity, of acceptance of a standard set of views complete with cliche answers to every objection, of smug self-satisfaction at belonging to an in-group. The closest similar experience I have ever had was at Cambridge, England, and even that was a distant second.
The homogeneity and provincialism of the New York intellectual community made them pushovers in discussions about Goldwater’s views. They had cliche answers but only to their self-created straw-men. To exaggerate only slightly, they had never talked to anyone who really believed, and had thought deeply about, views drastically different from their own. As a result, when they heard real arguments instead of caricatures, they had no answers, only amazement that such views could be expressed by someone who had the external characteristics of being a member of the intellectual community, and that such views could be defended with apparent cogency. Never have I been more impressed with the advice I once received: “You cannot be sure that you are right unless you understand the arguments against your views better than your opponents do.
{ Milton Friedman | via EconLog }
ideas, new york | October 12th, 2012 12:28 pm

If you could only ask one question to determine the IQ (g) of a person, what would it be?
[…]
“I’m going to give you five minutes,” he told me. “When I come back, I want you to explain to me something complicated that I don’t already know.” He then rolled out of the room toward the snack area. I looked at Cindy. “He’s very curious about everything,” she told me. “You can talk about a hobby, something technical, whatever you want. Just make sure it’s something you really understand well.”
{ Quora | Continue reading }
related { How do I get over my low tolerance for stupid people? }
photo { George Kelly }
guide, ideas | October 10th, 2012 7:55 am

Heaven is hotter than hell
Proof:
The temperature of heaven can be rather accurately computed. Our authority is the Bible, Isaiah 30:26 reads,
Moreover, the light of the moon shall be as the light of the sun and the light of the sun shall be sevenfold as the light of seven days.
Thus, heaven receives from the moon as much radiation as the earth does from the sun, and in addition seven times seven (forty nine) times as much as the earth does from the sun, or fifty times in all. The light we receive from the moon is one ten-thousandth of the light we receive from the sun, so we can ignore that. With these data we can compute the temperature of heaven: The radiation falling on heaven will heat it to the point where the heat lost by radiation is just equal to the heat received by radiation. In other words, heaven loses fifty times as much heat as the earth by radiation. Using the Stefan-Boltzmann fourth power law for radiation
(H/E)4 = 50
where E is the absolute temperature of the earth, 300°K (273+27). This gives H the absolute temperature of heaven, as 798° absolute (525°C).
The exact temperature of hell cannot be computed but it must be less than 444.6°C, the temperature at which brimstone or sulfur changes from a liquid to a gas. Revelations 21:8: But the fearful and unbelieving… shall have their part in the lake which burneth with fire and brimstone.” A lake of molten brimstone [sulfur] means that its temperature must be at or below the boiling point, which is 444.6°C. (Above that point, it would be a vapor, not a lake.)
We have then, temperature of heaven, 525°C. Temperature of hell, less than 445°C. Therefore heaven is hotter than hell.
Refutation:
In Applied Optics (1972, 11 A14) there appeared a calculation of the respective temperatures of Heaven and Hell. That of Heaven was computed by substituting the values given in Isaiah 30 26 in the Stefan-Boltzman radiation law. […] This is hard to find fault with. The assessment of the temperature of Hell stands, I suggest, on less firm ground.
{ Applied Optics/Journal of Irreproducible Results | Continue reading }
photo { Harold Diaz }
allegories, archives, fire, mathematics | October 9th, 2012 6:17 am

One of the many consequences of global warming is that it’s now, for the first time, possible to drill under the sea bed of the Arctic ocean. The oil companies are all there, of course, running geological tests and bickering with each other about the potential environmental consequences of an oil spill. But they’re not the only people drilling. Because there’s something even more valuable than oil just waiting to be found under the Arctic.
What is worth so much money that three different consortiums would spend billions of pounds to retrofit icebreakers and send them into some of the coldest and most dangerous waters in the world? The answer, of course, is information.
A couple of days ago, I called a friend in Tokyo, and we had a lovely chat. If he puts something up on Twitter, I can see it immediately. And on the web there are thousands of webcams showing me what’s going on in Japan this very second. It doesn’t look like there’s any great information bottleneck there: anything important which happens in Japan can be, and is, transmitted to the rest of the world in a fraction of a second.
But if you’re a City trader, a fraction of a second is a veritable eternity. Let’s say you want to know the price of a stock on the Tokyo Stock exchange, or the exact number of yen being traded for one dollar. Just like the light from the sun is eight minutes old by the time it reaches us, all that financial information is about 188 milliseconds old by the time it reaches London. That’s zero point one eight eight seconds. And it takes that much time because it has to travel on fiber-optic cables which take a long and circuitous route: they either have to cross the Atlantic, and then the US, and then the Pacific, or else they have to go across Europe, through the Middle East, across the Indian Ocean, and then up through the South China Sea between China and the Philippines.
But! If you can lay an undersea cable across the Arctic, you can save yourself about 5,000 miles, not to mention the risk of routing your information past a lot of political flash points. And when you’re sitting in your office in London and you get that dollar/yen exchange rate from Tokyo, it’s fresh from the oven, comparatively speaking: only 0.168 seconds old. If everybody else is using the old cables and you’re using the new ones, then you have somewhere between 20 milliseconds and 60 milliseconds when you know something they don’t.
Those are periods of time so short that humans can barely notice them. This essay, for instance, is about 900,000 milliseconds long, and it takes me hundreds milliseconds just to say the word “cable”. Which is a word with more than one meaning. To you, it probably means some kind of wire. But to City traders, it means 1.6254, or something very close to that number. Because in the City, “cable” means the pound/dollar exchange rate. And it’s named that after a transatlantic cable which was used to telegraph the exchange-rate information from London to New York as far back as 1858. […]
Obviously, only computer algorithms can make money from an information advantage which is measured in milliseconds. It’s computers which are making the decisions to buy and sell: if they had to wait for a human to sign off on those things, they’d never make any money at all. […] The more obvious problem with exchanges run by computers is that computers don’t have any common sense.
{ Felix Salmon/Reuters | Continue reading }
photo { Edward Weston }
economics, ideas, technology, traders, within the world | October 9th, 2012 4:14 am
ideas, mathematics | October 8th, 2012 7:36 am

What number is halfway between 1 and 9? Is it 5 — or 3?
Ask adults from the industrialized world what number is halfway between 1 and 9, and most will say 5. But pose the same question to small children, or people living in some traditional societies, and they’re likely to answer 3.
Cognitive scientists theorize that that’s because it’s actually more natural for humans to think logarithmically than linearly: 30 is 1, and 32 is 9, so logarithmically, the number halfway between them is 31, or 3. Neural circuits seem to bear out that theory. For instance, psychological experiments suggest that multiplying the intensity of some sensory stimuli causes a linear increase in perceived intensity.
In a paper that appeared online last week in the Journal of Mathematical Psychology, researchers from MIT’s Research Laboratory of Electronics (RLE) use the techniques of information theory to demonstrate that, given certain assumptions about the natural environment and the way neural systems work, representing information logarithmically rather than linearly reduces the risk of error.
{ MIT | Continue reading }
photo { Rupp Worsham }
ideas, mathematics, spinoza | October 6th, 2012 10:58 am
Courts are rarely asked to judge beauty. Such a subjective practice would normally be anathema to the ideal of objective legal standards. However, one area of federal law has a long tradition of explicitly requiring courts to make aesthetic decisions: the law of design. New designs may be protected as design patents, but only if they are “ornamental” in nature. As the U.S. Supreme Court has noted, “a design must present an aesthetically pleasing appearance…” This study uses empirical and experimental approaches to test the hypothesis that courts tend to favor more attractive patented designs over less attractive ones. It relies upon a data set that includes all design patent decisions from 1982 until 2010 in which a court made a final determination of validity or infringement, with every design patent at issue therein classified as valid or invalid and infringed or not infringed.
{ Journal of Intellectual Property Law/SSRN | Continue reading }
unrelated { The nuns in Catholic school taught us there was such a thing as sanctuary — the police cannot arrest a suspect in a church. Does this concept have a basis in law, or is it just a social custom that can be discarded on a whim? | The Straight Dope | full story }
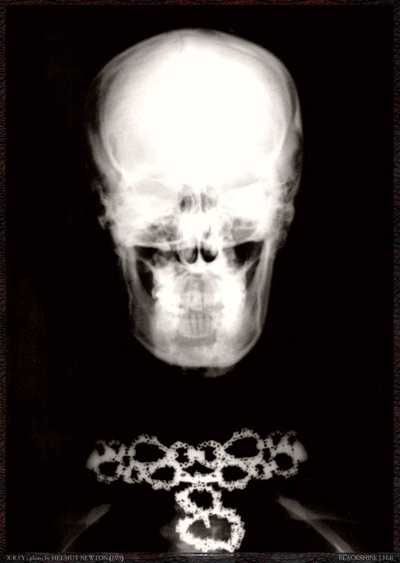
photo { Helmut Newton, Van Cleef & Arpels Diamond Necklace X-Ray, 1979 }
ideas, law | October 5th, 2012 11:17 am