traders
When Alex Goldstein was just 7 years old, he says, he was drawn to extreme weather. Within 10 years, he convinced his father to take him storm chasing and hasn’t stopped since.
Now, at 35, he leads a small group of data scientists and meteorologists who help teams of traders at one of the world’s largest hedge funds position themselves in commodities markets.
Millennium Management’s Goldstein and other specialists like him who can help model weather patterns in an increasingly volatile climate have become one of the most sought-after groups for hedge funds and trading firms. […]
Hedge funds on average hired 23% more weather experts, including data scientists and meteorologists, in 2024 compared to a year earlier. […] The average pay package has also increased by 18%, with the top talent getting as much as between $750,000 and $1 million.
That compares to a median salary in 2023 of about $93,000 for atmospheric scientists, including meteorologists, according to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics.
{ Bloomberg | Continue reading }
unrelated { IRS staff cuts mean less scrutiny for ultra-wealthy }
climate, economics, traders | March 12th, 2025 9:34 am
I think a lot about what I sometimes call “abstract commodity space.” Sometimes you want to buy nickel or aluminum or coffee or cocoa to make batteries or beer cans or cappuccino or chocolate bars, so you go to some supplier and negotiate a contract for the delivery of a useful amount of a particular grade of the commodity to your factory. Sometimes, though, you want to bet on the price of nickel or aluminum or coffee or cocoa, to hedge some risk to your business or just as a speculative bet. So you buy commodity futures, financial assets that reflect the price of a commodity but don’t require you to store it or worry about it spoiling.
The way these futures often work is that there are big warehouses full of the commodity, and people write futures contracts that essentially transfer the entitlements to the commodities in the warehouse, without ever having to take them out. Your futures represent a claim on some nickel or coffee in a warehouse in abstract commodity space,[1] and you don’t have to think much about the physical properties of the actual thing. The warehouse system has put a layer of abstraction on the messy commodity business, and you can treat the commodity as just a number on your computer screen.
We mostly talk about this when it breaks down, though. Sometimes the physical world tears through the layer of abstraction. The coffee or cocoa beans are stale, or someone discovers that the nickel in the warehouse is actually a bag of rocks.
Or: Abstract commodity space is fairly global, and you can trade abstract commodities from a computer screen anywhere in the world. But the physical world is not so seamlessly globalized. Now, gold in a warehouse in New York is worth more than gold in a warehouse in London. Here’s a Wall Street Journal article on “Why Dealers Are Flying Gold Bars by Plane From London to New York”:
Gold is, for the moment, worth substantially more in Manhattan than in the U.K. capital, sparking the biggest trans-Atlantic movement of physical bars in years. Traders at major banks are racing to yank gold from vaults deep below London’s medieval streets and from Swiss gold refineries and ferry them across the ocean. …
Banks run big offsetting positions, owning gold bars in London, lending them out to earn a return and hedging the risk that prices fall by selling futures in New York. JPMorgan and HSBC, which clear gold transactions and store bullion for other banks in London, are the biggest players in this trans-Atlantic market.
Banks run big offsetting positions, owning gold bars in London, lending them out to earn a return and hedging the risk that prices fall by selling futures in New York. JPMorgan and HSBC, which clear gold transactions and store bullion for other banks in London, are the biggest players in this trans-Atlantic market.
The trade appears almost risk-free as long as prices on both sides of the Atlantic are close to each other. But when prices on the Comex surged above those in London late last year, baking in possible tariffs, contracts that the banks had sold in New York were suddenly underwater. …
Banks could close the trade by buying futures in New York, but such a move would mean crystallizing those losses. Another alternative: flying the physical gold they owned in London to New York and delivering it to the futures contracts’ owners instead. […]
Comex contracts require a different size of bar, so traders need to send gold to Swiss refiners to recast it before flying on to the U.S. Sometimes, they cut out the first European leg by handing the refiner gold in London in exchange for the right size of bar, or flying bullion in from Australia instead.
{ Matt Levine | Continue reading }
traders | February 13th, 2025 1:20 pm

DeepSeek’s origins are in finance, not technology for technology’s sake. Its parent company, a Chinese hedge fund called High-Flyer, began not as a laboratory devoted to safeguarding humanity from A.I. like Open AI, but as a business using A.I. to make bets in the Chinese stock market.
{ NY Times | Continue reading }
The nice thing about building an artificial intelligence model out of a quantitative hedge fund is that there are interesting ways to monetize it. A standalone AI company will probably think of ideas like “sell subscriptions to an AI chatbot” or “sell access to an application programming interface,” but with a hedge fund you can be more creative. […]
There is a much funnier approach. […]
• Build a good AI model that can compete with the leading large language models built by tech giants, but cheaply, with fewer and less sophisticated chips and less electricity.
• Sell short the stocks of the tech giants with expensive AI models, and the big chipmakers, and electric utilities and everyone else who is exposed to the “AI is a gusher of capital spending” trade.
• Then announce your cheap good open-source model.
• Wipe out almost $1 trillion of equity market value, and take some of that for yourself.
I have no reason to think that quant fund manager and DeepSeek founder Liang Wenfeng actually did that, or even thought about it, but, man, wouldn’t it be cool if he did?
{ Matt Levine/Bloomberg | Continue reading }
oil on canvas triptych painting { Francis Bacon, Triptych Inspired by the Oresteia of Aeschylus, 1981 }
related { interview with Liang Wenfeng, founder and CEO of Deepseek }
robots & ai, traders | January 28th, 2025 12:21 pm

In January 2023, short seller Hindenburg Research put out a report claiming that executives at one of India’s largest conglomerates were manipulating the company’s stock price.
The Adani Group and its multibillionaire founder Gautam Adani strenuously deny the accusations, but the report instantly wiped off as much as $140bn from the conglomerate’s market value and sent ripples through the country’s establishment. It also catapulted the New York-based Hindenburg and its founder Nathan Anderson into Wall Street lore.
Few saw it coming. But one that did was a hedge fund in New York almost 13,000 kilometres away from the Indian conglomerate’s headquarters.
Kingdon Capital Management had received a draft of the short seller’s report in November 2022 as part of an agreement it had signed with Hindenburg a year earlier, India’s markets regulator revealed in June.
The hedge fund, which was founded by Mark Kingdon in the 1980s, had set up a special fund in Mauritius and had started building a short position on Adani two weeks before Hindenburg released its report.
Kingdon, which has less than $1bn in assets under management, turned a $22mn profit from the trade. As part of the agreement, Hindenburg received a 25 per cent cut of the spoils. […]
activist short sellers tend to explicitly look for evidence suggesting malfeasance. […] Hindenburg, for example, says that it seeks out situations where there might be some combination of accounting irregularities, undisclosed related-party transactions, and illegal or unethical business or financial reporting practices.
{ Financial Times | Continue reading }
oil on canvas { Francis Bacon, Man in blue IV, 1954 }
Francis Bacon, traders | November 21st, 2024 1:51 pm
Shareholder democracy is weird because you can just buy votes. In fact, that’s kind of the point: Each share of a public company usually has one vote, so if you want to take control of the company, all you have to do is buy enough shares to win a shareholder vote. (Conservatively 50% plus one, but probably less, if you can get other shareholders to join you and/or they don’t vote.) The voting power is generally proportional to the economic ownership of the company; the more you own, the more say you have.
But it is reasonably easy to hedge stock. If you own a lot of stock of a company, and you want to (1) continue owning that stock but (2) not be fully economically exposed to the risk of the stock price, you can probably find a way to do that. Most simply, you could (1) buy 10 million shares of stock and (2) also borrow 10 million other shares of stock and sell them short. You’re long 10 million shares and short 10 million shares, so you have net zero exposure: If the stock goes up (or down), you will make (lose) money on the 10 million shares you own, and lose (make) an exactly offsetting amount of money on the 10 million shares that you are short. But you get to vote the 10 million shares that you’re long, while you don’t get negative votes for shares you are short. So you have zero economic ownership but 10 million votes. […]
The fun question, which people email me about from time to time, is: What if you go long 10 million shares and short 20 million shares? Then (1) you get to vote 10 million shares and, as a big economic owner, you have a say in the running of the company, but (2) you actually profit if the company does badly, so your voting incentives will be bad.
{ Matt Levine / Bloomberg | Continue reading }
economics, traders | November 19th, 2024 12:41 pm
Christopher DeVocht, a carpenter from Vancouver Island, Canada, says he started out like a lot of day traders. After work, he’d read about trading on forums. His favorite things to trade were options on Tesla Inc. stock. […]
At the end of 2019, his account, with the brokerage division of Royal Bank of Canada, was worth C$88,000. Within two years, he’d turned that into C$415 million ($306 million), he says.
Some people would have cashed out. DeVocht didn’t. And when Tesla stock fell in 2022, he lost it all. […]
DeVocht now claims that the advice he received, geared mainly toward minimizing taxes, was negligent […] [Royal Bank of Canada] advised him to incorporate a company, roll all of his securities into it and conduct trades within the company “with a strategy of accumulating as many Tesla shares as possible and holding them for as long as possible,” DeVocht claims in the lawsuit. The idea was to convince Canadian tax authorities to view it as an investment holding company, not an active trading business, because he’d pay lower taxes that way.
{ Bloomberg | Continue reading }
traders | October 7th, 2024 12:24 pm
This is just a cool insider trading case. There’s a guy, Robert Westbrook. He allegedly hacked into the email accounts of several executives at different US public companies. The SEC complaint lays out how he allegedly did that:
He would go to the executive’s Outlook email login page and click to reset the password. “Four of the five Hacked Companies used the same password reset portal software,” says the SEC, and he was apparently familiar with its workings.
He subscribed to “an online directory service provider and an online genealogy company,” which gave him “personal and family
information that could be used to guess the answers to the security questions that employees at the Hacked Companies may have used to reset their passwords.” You can do a lot of damage if you know a public-company executive’s mother’s maiden name and first pet’s name.
He’d reset their passwords and get access to their emails.
Then he’d read them and look for secret earnings information. […]
But even if you get earnings releases in advance, there’s no guarantee that you’ll make money. My Bloomberg Opinion colleague John Authers wrote last week about an Elm Partners study finding that most people can’t trade profitably even knowing tomorrow’s news. […]
Ten trades were winners, four were losers, the winners were bigger than the losers and his net profit was about $3.4 million. […]
This includes buying half a million dollars’ worth of one company’s[2] stock and call options before its March 2019 earnings report, and making a $236,492 profit when the earnings were good, and then buying $786,364 worth of that company’s put options before its March 2020 earnings report, and making a $1.04 million profit when those earnings were mixed.
{ Matt Levine / Bloomberg | Continue reading }
scams and heists, traders | October 1st, 2024 12:53 pm
• You buy a stock, its value keeps going up, you don’t sell it and you don’t pay taxes.
• If you need cash, you go to your broker and take out a loan, secured by the value of the stock.
• If the stock keeps going up, you never pay back the loan, and you can borrow more money if you want.
• Eventually you die, your heirs get the stock, and they don’t pay taxes on your gains. (This is called the “basis step-up”: When you inherit stock, the IRS pretends that you paid market value for it, so you don’t have to pay taxes on the previous gains.)
This is sometimes called the “buy, borrow, die” tax strategy.
{ Bloomberg/Matt Levine | Continue reading }
economics, traders | December 4th, 2023 2:25 pm

Nomura and Credit Suisse are facing billions of dollars in losses after a U.S. hedge fund, named by sources as Archegos Capital, defaulted on margin calls. […]
A margin call is when a bank asks a client to put up more collateral if a trade partly funded with borrowed money has fallen sharply in value. If the client cannot afford to do that, the lender will sell the securities to try to recoup what it is owed.
Margin calls on Archegos Capital prompted a massive unwinding of leveraged equity bets. Shares in ViacomCBS and Discovery each tumbled around 27% on Friday, while U.S.-listed shares of China-based Baidu and Tencent Music plunged during the week, dropping as much as 33.5% and 48.5%, respectively, from Tuesday’s closing levels. […]
Morgan Stanley sold $4 billion worth of shares early on Friday, followed by another $4 billion in the afternoon. […] Goldman liquidated more than $10 billion worth of stocks in the block trades [and] sold $6.6 billion worth of shares of Baidu Inc, Tencent Music Entertainment Group and Vipshop Holdings Ltd, before the U.S. market opened on Friday […] Following this, Goldman sold $3.9 billion worth of shares inViacomCBS Inc, Discovery Inc, Farfetch Ltd, iQIYI Inc and GSX Techedu Inc […]
Hwang, who founded Archegos and ran Tiger Asia from 2001 to 2012, renamed it Archegos Capital and made it a family office.
{ Reuters | Continue reading }
Archegos borrowed a mere five times its capital. Closely regulated Goldman Sachs is at nearly seven times on a risk-weighted basis. […]
Hwang himself was a walking risk factor. He admitted to wire fraud in 2012 and in 2014 was banned from trading in Hong Kong for four years.
{ Reuters | Continue reading }
traders | March 29th, 2021 12:32 pm
haha, traders | January 28th, 2021 8:20 pm

Data analytics company Palantir Technologies and workplace software maker Asana Inc are set to debut on the U.S. stock market on Wednesday bypassing an initial public offering (IPO). […]
[S]ome investors and corporate executives have been pushing to shed investment banks as their middlemen. For years, they have criticized IPOs as chummy deals that allowed bankers to allocate the most shares to their top clients. […] “If Palantir and Asana are successful, which they should be, more and more companies will return to looking seriously at direct listings,” Narasin added. […]
In 2020, the price of a newly listed company’s shares has risen by an average of 38% on the first day of trading, according to IPOScoop data and Reuters calculations.
This has fueled renewed criticism among investors snubbed by the investment banks underwriting the IPOs, as well as suspicion among some companies that bankers are leaving money on the table in their IPO to help create a first-day trading “pop”. […]
In a direct listing, no shares are sold in advance, as is the case with IPOs. The company’s share price in its market debut is determined by orders coming into the stock exchange.
The downside is that the companies involved cannot raise money, though both NYSE and Nasdaq have requested U.S. regulators allow them to change their rules to allow companies to sell new stock in a direct listing.
{ Reuters | Continue reading }
traders | September 29th, 2020 8:24 am

“Financial machine learning creates a number of challenges for the 6.14 million people employed in the finance and insurance industry, many of whom will lose their jobs — not necessarily because they are replaced by machines, but because they are not trained to work alongside algorithms,” said Marcos Lopez de Prado, a Cornell University professor. […]
Nasdaq runs more than 40 different algorithms, using about 35,000 parameters, to look for market abuse and manipulation in real time.
{ Bloomberg | Continue reading }
related { 90% of high-tech job growth concentrated in just 5 cities: Boston, San Francisco, San Jose, Seattle and San Diego }
photo { Matthew Reamer }
economics, photogs, robots & ai, traders | December 10th, 2019 9:42 am

Software from Amenity Analytics promises to automate this process by spotting when chief executive officers try to duck tough questions. The software, its makers say, can even pick up on the signs of potential deception that CIA and FBI interrogators look for—including stalling and the use of qualifiers—and can gauge the sentiment of what is said on calls and reported in public filings, issuing a positive or negative numeric score. The goal is to make it easier for investors to wade through information and quickly make trading decisions.
{ Bloomberg Businessweek | Continue reading }
previously { Former CIA Officer Will Teach You How to Spot a Lie }
photo { Laurie Simmons, Blonde/Pink Dress/Standing Corner, 2014 }
psychology, technology, traders | April 22nd, 2019 6:58 am
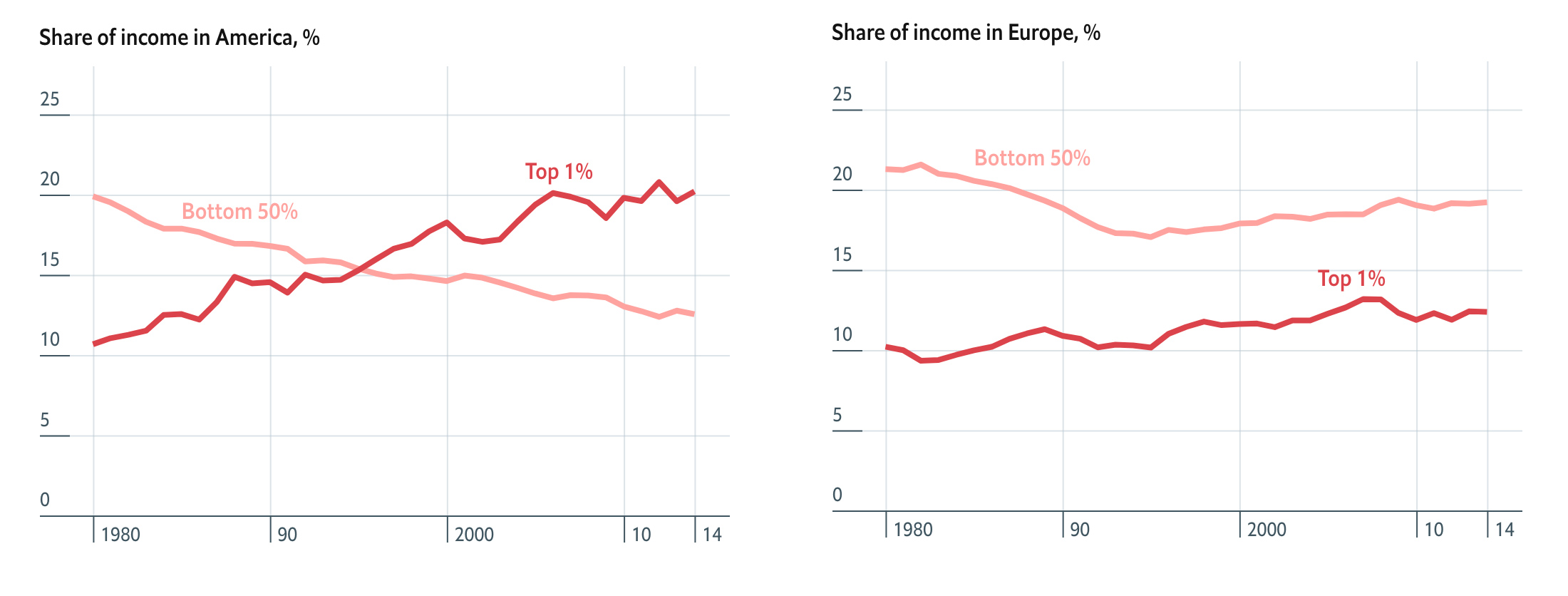
{ while ordinary people are struggling, those at the top are doing just fine. Income and wealth inequality have shot up. The top 1% of Americans command nearly twice the amount of income as the bottom 50%. The situation is more equitable in Europe, though the top 1% have had a good few decades. | The Economist | full story }
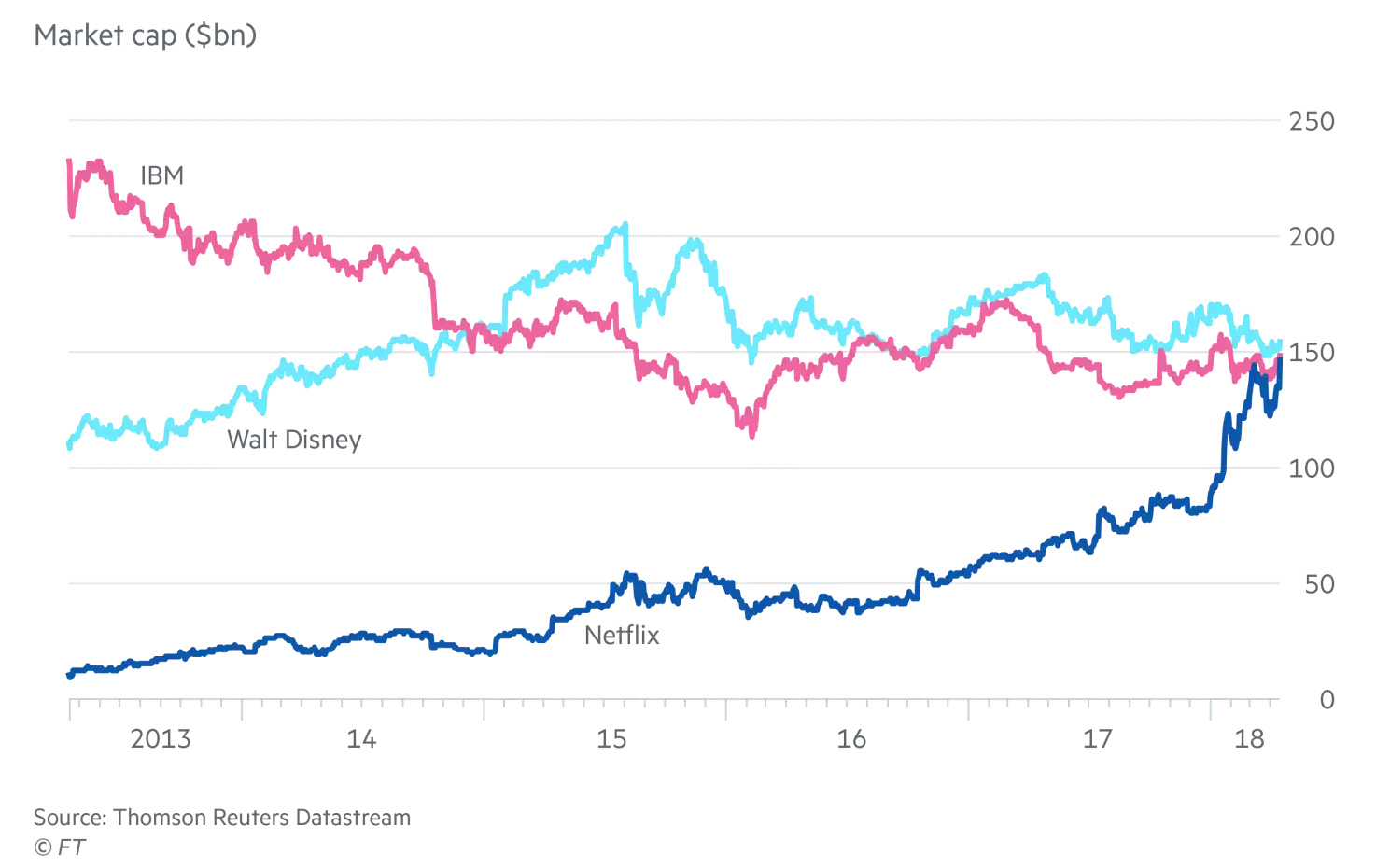
{ Netflix performance burns hedge fund short sellers }
economics, showbiz, traders | April 18th, 2018 10:12 am

Twelve years ago, my now-Bloomberg colleague Joe Weisenthal proposed that startups that planned to disrupt an established industry should short the stock of the incumbents in that industry. That way, if they were right — if they were able to undercut big established public companies — then they’d get rich as those public companies declined. […] Their profits would come from the incumbents’ shrinking.
Weisenthal’s proposal was for disruptors offering a free product; the idea was that the entire business model would consist of (1) offering a free service that public companies offer for money and (2) paying for the service by shorting the public companies. But there’s a more boring and more widely generalizable — yet still vanishingly rare — version of this approach in which it just augments the disruptors’ business model: You sell better widgets cheaper and make a profit that way, while doubling down by also shorting your competitors. It’s a more leveraged way to do the business you were going to do anyway, an extra vote of confidence in yourself.
{ Bloomberg | Continue reading }
economics, traders | April 16th, 2018 10:33 am
You know, someone invented the XIV ETN. And someone invented the VIX, and VIX futures. And when you read the technical specifications for all of those things, it is clear that they are not trivial feats of engineering. Teams of marketers and traders and quants and technologists and lawyers put many hours into getting them just right, so that they would work as intended. They are technologies, highly engineered tools designed to help customers do things that they couldn’t have done before. They are financial technologies, built not out of screens and circuit boards but out of formulas and hedging strategies and legal documents, but that is what you’d expect: Financial firms ought to innovate in financial technology.
Yesterday Goldman Sachs Group Inc. Chief Executive Officer Lloyd Blankfein presented at the Credit Suisse Financial Services Conference, and his presentation is kind of a weird read. The running theme is that Goldman is doing technology stuff to win business. “Engineering underpins our growth initiatives,” says a summary page, and it doesn’t mean financial engineering. In fixed income, currencies and commodities, engineers are 25 percent of headcount, and the presentation touts growth in Marquee (its client-facing software platform) and “systematic market making.” In equities, Goldman touts its quant relationships. In consumer banking (now a thing!), the centerpiece is Marcus, Goldman’s online savings and lending platform. And in investment banking, “Engineering enhances client engagement through apps, machine learning and big data analytics.” […]
Instead of developing new financial technologies, Goldman is developing new computer technologies for its financial clients.
{ Bloomberg | Continue reading }
related { Hedge-fund mediocrity is the best magic trick. Never have so many investors paid so much for such uninspiring returns. }
lithograph { Ellsworth Kelly, Camellia III, 1964–65 }
economics, traders | February 15th, 2018 1:39 pm
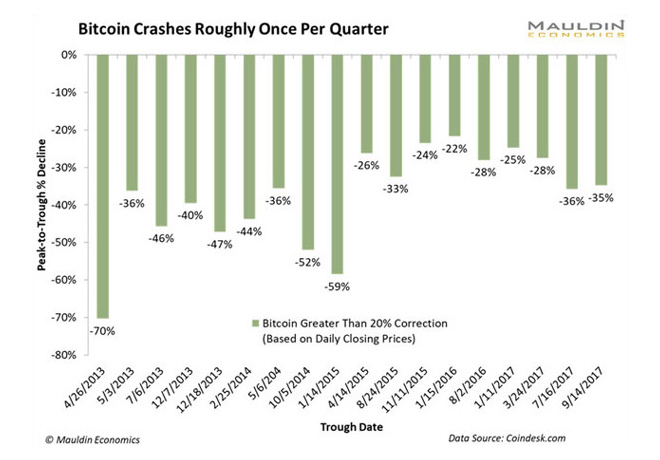
There are 1,036 virtual currencies out there, from Bitcoin to — no joke — BigBoobsCoin. The price of almost every single one was down Friday morning.
{ Bloomberg | Continue reading }
cryptocurrency, traders | December 23rd, 2017 11:37 am

Stock trading strategies: competition is so stiff that there are only two ways to succeed: (1) insider trading, e.g. you try to obtain job interviews with small publicly traded companies, then based on information glanned during the interview, perform trades and (2) use trading strategies that professional traders will never use, e.g. stay “all cash” for several years on your trading account, and when the right event occurs, massively trade major indexes for a couple of days, then go dormant for another few years. You need sophisticated statistical models to succeed in this, with good back testing, walk-forward and robustness based on state-of-the-art cross-validation.
{ analyticbridge | Continue reading }
art { Rochelle Goldberg, The Cannibal Actif, 2015 }
economics, traders | November 14th, 2016 12:24 pm

Two hedge fund “quants” have come up with an algorithm that diagnoses heart disease from MRI images, beating nearly 1,000 other teams in one of the most ambitious competitions in artificial intelligence.
{ Financial Times | Continue reading }
Qi Liu and Tencia Lee, hedge fund analysts and self-described “quants,” didn’t know each other before they won the competition, beating out more than 1,390 algorithms. They met each other in a forum on the Kaggle site, where the competition was hosted over a three-month period.
{ WSJ | Continue reading }
health, technology, traders | June 24th, 2016 7:41 am
The mantra of Wall St hedge funds was once “only the strongest will survive.” It may now have to change to “the geeks will inherit the earth.”
Hedge fund “quants” who use computer systems to trade financial markets earned more money than some of the industry’s most famous stockpickers, who posted large losses in 2015.
The most prominent among the quants was string theory expert and former code breaker James Simons of Renaissance Technologies, who earned $1.7bn, putting him in joint first place.
He was joined in the top 10 earners by former Columbia University computer science professor David Shaw of DE Shaw who made $750m and John Overdeck and David Siegel of Two Sigma who made $500m each.
Their success came in stark contrast to some of the biggest names on Wall Street who rely on human investment judgment rather than lines of computer code.
{ FT | Continue reading }
quote { Cabinet magazine | full story }
technology, traders | May 10th, 2016 3:13 pm