‘Le sage arrose doucement, l’insensé tout de suite inonde.’ –Florian
The group, known to researchers as “Dragonfly” or “Energetic Bear” for its hackings of the energy sector, was not involved in 2016 election hacking. But it has in the past five years breached the power grid, water treatment facilities and even nuclear power plants, including one in Kansas.
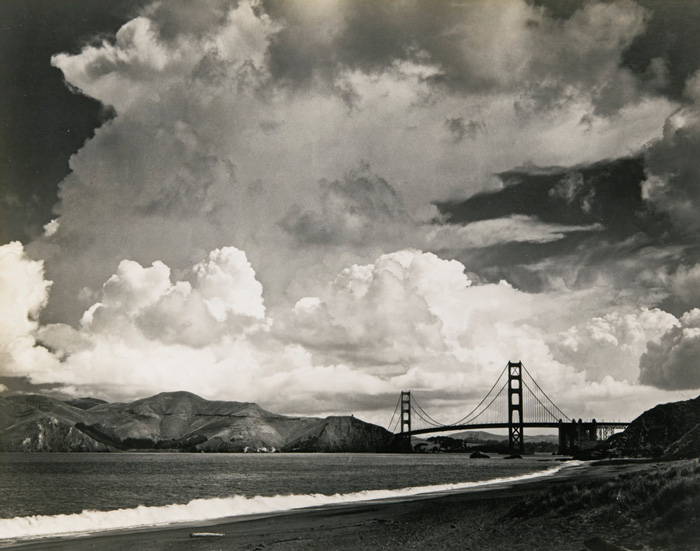
It also hacked into Wi-Fi systems at San Francisco International Airport and at least two other West Coast airports in March in an apparent bid to find one unidentified traveler, a demonstration of the hackers’ power and resolve.
September’s intrusions marked the first time that researchers caught the group, a unit of Russia’s Federal Security Service, or F.S.B., targeting states and counties. The timing of the attacks so close to the election and the potential for disruption set off concern inside private security firms, law enforcement and intelligence agencies. […]
“This appears to be preparatory, to ensure access when they decide they need it,” […] Energetic Bear typically casts a wide net, then zeros in on a few high-value targets. […] They could take steps like pulling offline the databases that verify voters’ signatures on mail-in ballots, or given their particular expertise, shutting power to key precincts. […]
Officials at San Francisco International Airport discovered Russia’s state hackers had breached the online system that airport employees and travelers used to gain access to the airport’s Wi-Fi. The hackers injected code into two Wi-Fi portals that stole visitors’ user names, cracked their passwords and infected their laptops. The attack began on March 17 and continued for nearly two weeks until it was shut down. […] As pervasive as the attacks could have been, researchers believe Russia’s hackers were interested only in one specific person traveling through the airports that day.